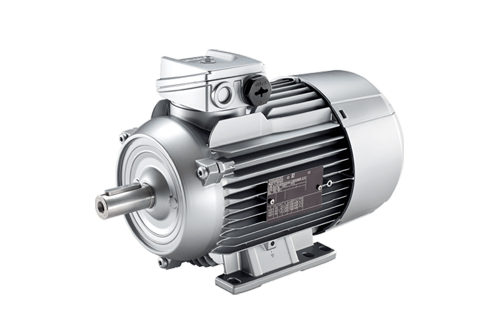
AC Motor
Price 5000 INR/ Unit
AC Motor Specification
- Voltage
- 220-240 Volt (v)
- Frequency (MHz)
- 50-60 Hertz (HZ)
- Protect Feature
- Waterproof
- Phase
- Three Phase
- Speed
- 1400 RPM
- Starting Type
- Electric Start
- Power
- 220 Volt (v)
- Color
- Sliver
- Weight
- 200-500 Kilograms (kg)
- Warranty
- 1 Year
AC Motor Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Unit
- Supply Ability
- 5 Units Per Day
- Delivery Time
- 1 Week
- Packaging Details
- Wooden Box.
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About AC Motor
An AC motor, or an alternating current motor, is a type of electric motor that operates using AC power. AC motors are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including industrial machinery, household appliances, and transportation systems.
The basic principle behind the operation of an AC motor is the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents. AC motors are typically made up of two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator is a stationary component that consists of a series of coils of wire, while the rotor is a rotating component that is typically made up of a series of conductive bars or plates.
When an AC current is passed through the stator, it creates a magnetic field that rotates around the stator. This magnetic field induces a current in the rotor, which then creates its own magnetic field that interacts with the stator's magnetic field. The interaction between the two magnetic fields causes the rotor to turn, which drives the motor's mechanical output.
There are several different types of AC motors, including synchronous and asynchronous (or induction) motors. Synchronous motors operate at a fixed speed that is determined by the frequency of the AC power source and the number of poles in the motor. Asynchronous motors, on the other hand, are designed to run slightly slower than the synchronous speed and are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including pumps, fans, and compressors.
AC motors are generally more efficient and require less maintenance than DC motors. They are widely used in a wide range of applications due to their versatility and reliability, and are often used in conjunction with motor controllers or variable frequency drives to regulate their speed and improve their efficiency.
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
More Products in Abb Electric Motor/ Crompton Electric Motor/ Sieme Category
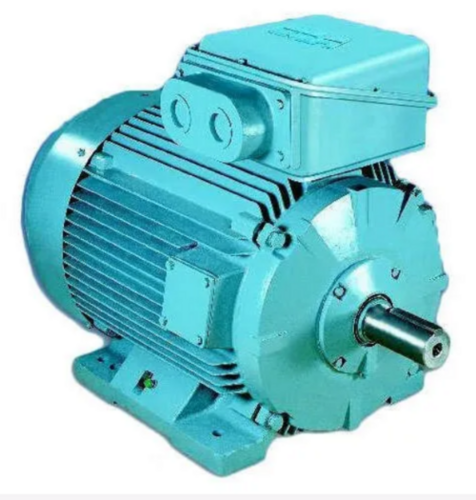
ABB MOTOR
Price 20000 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 10 Pieces
Product Type : Motor
Rated Voltage : 220/415 Volt (V)
Conductor : Copper
Sealed Type : Mechanical Seal
"We are only dealing in North India."
 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry

 Call Me Free
Call Me Free
